FAQs
Is chemical cauterization safe for benign eyelid lesions?
Chemical cauterization is a safe procedure when performed by trained professionals. It’s a precise, minimally invasive procedure that effectively removes benign lesions.
What types of eyelid lesions can be treated with chemical cauterization?
Chemical cauterization is typically used for benign skin lesions on the eyelids such as: Papilloma, Seborrheic Keratosis, Verruca, Xanthelasma or other non-cancerous growths.
How do I diagnose a benign eyelid lesion?
Diagnosing benign eyelid lesions requires a thorough clinical examination. Rely on the education and training you have received in order to become a licensed health care provider. When in doubt, refer for biopsy.
How long does it take for the lesion to heal after treatment?
Healing times can vary depending on the size and depth of the lesion, but typically, the lesion will begin to necrotize in 1-2 days. The lesion will usually scab over and fall off in 1-2 weeks.
Are there any side effects or complications to be aware of?
While chemical cauterization is generally safe, side effects can include temporary redness, swelling, or mild discomfort at the site of treatment. Rarely, scarring or slight depigmentation may occur.
What is the aftercare for a chemical cauterization procedure?
Post-treatment care typically includes keeping the area clean. However, once the lesion is treated with the chemical, it will necrotize and fall off regardless. There are no post operative ointments or medications needed
How do I determine if chemical cauterization is the best treatment option for my patient?
This decision should be based on the type, size, and location of the lesion, as well as the patient's overall health. If the lesion is small, superficial, and non-cancerous, chemical cauterization can be a highly effective and minimally invasive option.
Do I need patient consent before performing chemical cauterization?
Yes, informed consent is required. Patients should be educated about the procedure, its risks, benefits, alternatives, and the expected healing process.
How do I handle potential scarring after treatment?
If scarring occurs, it is usually minimal and fades with time. The best way to address this concern is patient education before treatment occurs.
Can this procedure be done in an office setting?
Chemical cauterization is a minimally invasive procedure that is typically performed in an office or clinic setting. Anesthesia is not needed.
How should I manage follow-up care after the procedure?
A follow-up appointment is typically scheduled 2 weeks after the procedure to ensure the lesion was treated completely and to check for any signs of infection or complications. In some cases, additional treatment may be needed.
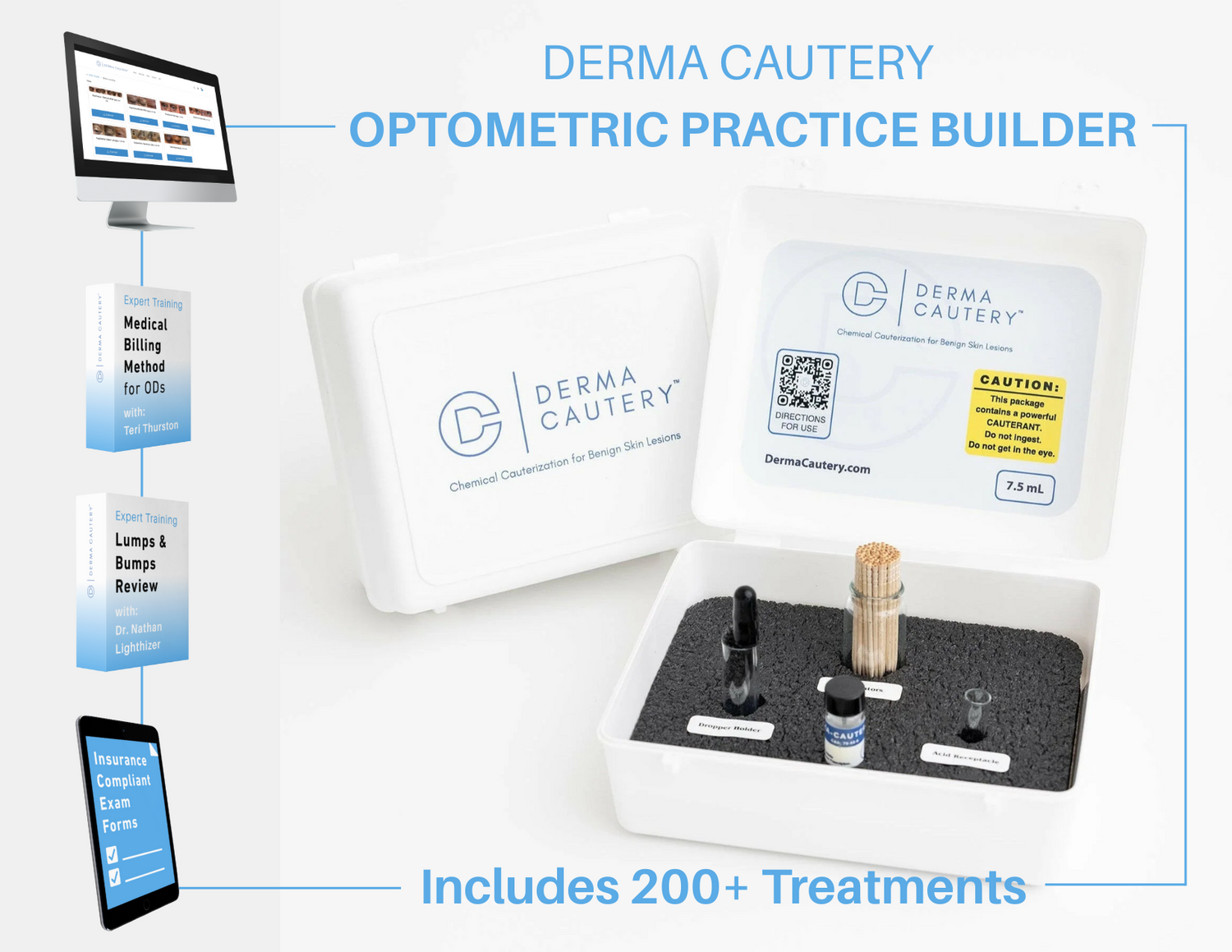
The Derma Cautery Solution
Add An Additional $70,000+ to Your Practice.
Use an Injection Free, Pain Free, 5-10 Minute Procedure.
Discover A Unique Way to Stand Out from Other ODs Offering Only Routine Exams